19 Mar Nail Fungus
Fungi which causes infection of our feet is everywhere in the environment. We all have fungus living on our feet and in our shoes, but not all of us get fungal infections. Areas which have high concentrations of fungus include damp areas such as public gyms, shower stalls and swimming pools. Athletes and people who wear tight-fitting shoes or tight hosiery that cause trauma to the toes or keep the feet from drying out are at higher risk. The condition can also spread from one toe to another, or to other parts of the body.
Other risk factors include abnormal PH level of the skin, not drying off the feet thoroughly after bathing or exercise, and a compromised immune system in someone who has been exposed to a fungus. Diabetics have an increased risk of contracting a toenail fungus because their immune system is compromised.
San Antonio as with other sub tropical areas, tend to have higher rates of fungus then colder cities. Podiatrist are typically the first specialist to diagnose and treat this condition.
Sypmtoms
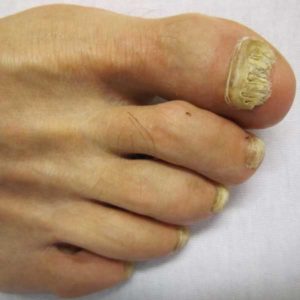
Thick, yellow toenails are due to nail fungus approximately 60% of the time. Other causes include nail root damage, metabolic disease, psoriasis and eczema. Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, affects millions of people world wide, and is most prevalent in warm climates. Fungi, which are microscopic organisms, typically thrive in warm, moist environments. A function of modern day society is the use of shoe gear. This also happens to be the perfect happy home for fungus. As a result, the incidence of nail fungus is much higher on the toes then on the hands.
Signs that you may have toenail fungus include thick, yellow toenails. You may also see redness and scaling to the bottom of your feet. This is known as a chronic athlete’s foot infection and is a result of infected toenails acting as a reservoir, constantly infecting your skin. Toenail color can vary from brown or yellow to white with this condition. It occurs most often on the big toe, but can easily spread throughout all of your toes.
Treatment
Because it is difficult to treat or eradicate toenail fungus, it is a good idea to try to prevent it. It helps to wear protective shoes or sandals in public showers, pool areas and gyms, and to avoid borrowing someone elses shoes or sharing socks or towels with someone who has toenail fungus. An orthotic device can be used to add cushioning and/or control over-pronation, support the longitudinal arch, and reduce stress on the lower leg muscles.
Wash your feet regularly, and dry them thoroughly when they get wet. Wearing nail polish on the toes is not advised because it can seal in fungus and allow it to grow. Keep toenails trimmed, and be sure to disinfect any pedicure tools before using them.
If you do develop toenail fungus, see your foot doctor. The podiatrist might remove as much of the nail as possible by trimming, filing or dissolving it. Medicated nail polish might be prescribed for a localized infection, but a serious infection will likely be treated with a prescription oral antifungal medication. These medications can have side effects, so be sure to work closely with your podiatrist on your treatment plan. Only in severe cases will surgical removal of the nail be recommended.
If you suspect that you have toenail fungus, see your podiatrist.

